RNAa
‘Turn up’ Transcription
RNAa uses short duplex RNA known as saRNA to target and ‘turn up’ transcription of an endogenous gene leading to
restoration of endogenous protein function.
RNAa Offers Unprecedented Advantages:
EXPANSION & RESTORATION
Broadening Therapeutic Horizons
Ractigen Therapeutics is redefining the approach to treating a wide range of diseases by focusing on the activation of beneficial genes, rather than merely targeting disease-causing ones. This strategy opens new avenues for conditions previously deemed undruggable by conventional methods, particularly those affected by epigenetic silencing or the downregulation of gene expression.
Faithful Restoration of
Natural Gene Function
EXPRESSION & ACCELERATION
Persistent Expression
of Target Gene
Acceleration of In-house
Drug Development
Pre-established medicinal chemistries and drug delivery platforms developed for gene silencing techniques are readily implemented accelerating in-house drug development.
COST REDUCTION & MAXIMIZATION
Our In-house Expedited and
Cost-saving Screening Process
Our in-house expedited and cost-saving screening process rapidly identifies numerous saRNAs for targeted genes of choice. Each represents a candidate API.
Maximize Transcriptional Output
Additional tweaks improve medicinal properties and maximize transcriptional output for selected lead candidates.
Mechanism of RNAa
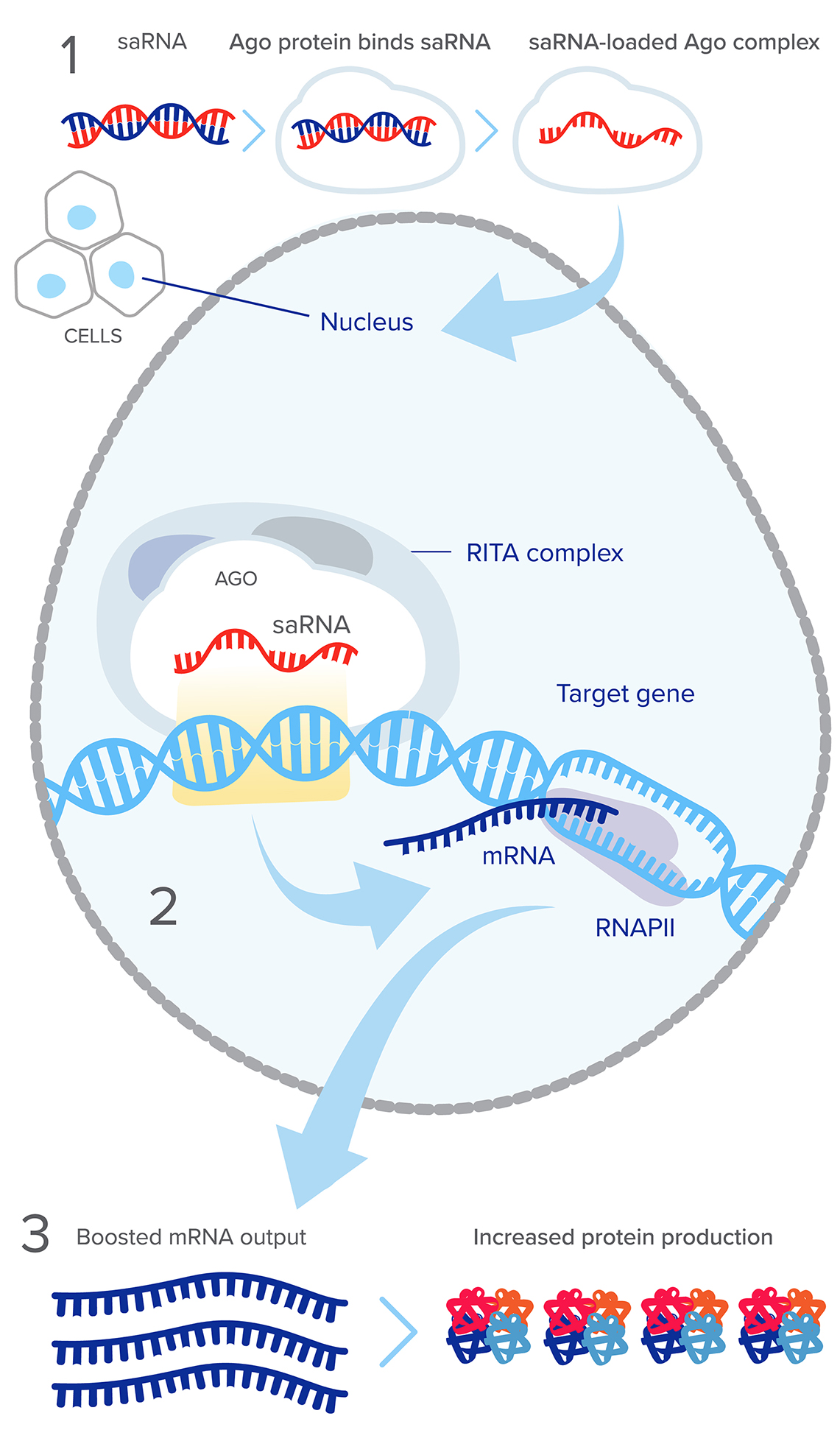
1: INPUT
saRNA Targets Non-coding Regulatory Sequence
saRNA is loaded into the AGO2 protein and processed into a single-strand.
2: SYSTEM
Cells with Target Endogenous Gene
AGO-saRNA complex enters the nucleus and recognizes a non-coding regulatory
sequence embedded in chromatin proximal to targeted gene and recruits
additional proteins to form the RITA complex.
3: OUTPUT
Elevated Target Gene Protein Levels
Formation of the RITA complex augments steps of transcription
initiation/elongation via RNAPII enrichment/ phosphorylation
and epigenetic modification indicative of relaxed chromatin.
Enhanced target gene transcription boosts mRNA output
leading to an increase in protein production.